Loreto
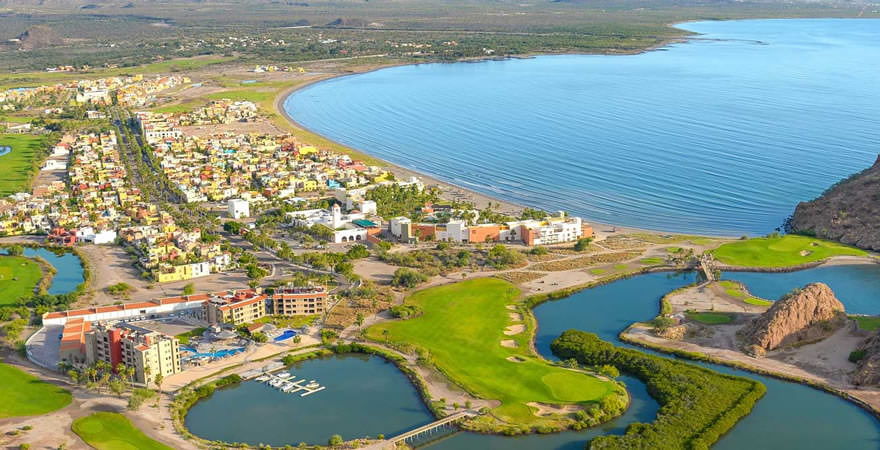
Loreto (or Conchó) is a city in and municipal seat of Loreto Municipality, located on the Gulf of California in eastern Baja California Sur state, Mexico.
The city of 14,724 people (2010 census) is located about 350 km (220 mi) north of La Paz, the capital of Baja California Sur state.
The city is a tourist resort, catering mostly to U.S. travelers.
Many American tourists enjoy fishing in “pangas” for “dorado” (Mahi-mahi or Dolphin Fish). Local restaurants will willingly prepare the daily catch of the tourists.
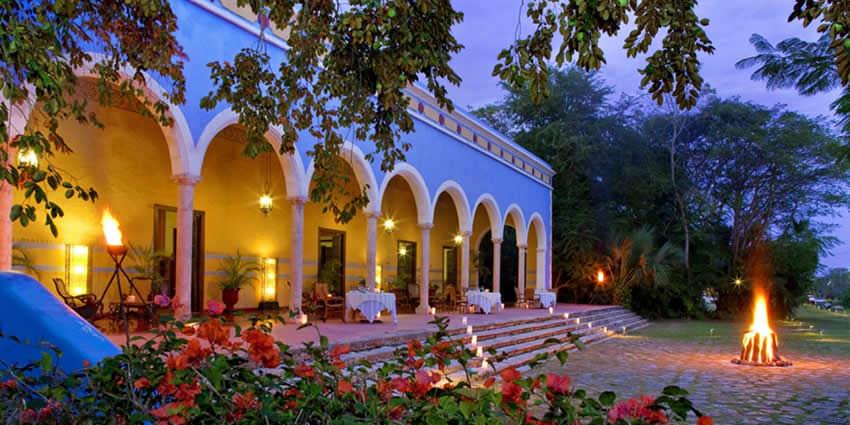
Loreto has a museum that coexists alongside the historic, but still active, parish.
Geo & Climate
Loreto is located on the east coast of the Baja California Peninsula. It is bordered on the east by the Gulf of California, on the west by the Transpeninsular Highway, and on the south by the Arroyo Loreto, a dry creek bed that only fills with water after a heavy rainfall.
The city is built on relatively flat land with an average elevation is 10 meters (33 ft) above sea level. “La Giganta” Mountain Range (“Sierra de la Giganta”) lies to the west, extending along the center of the state of Baja California Sur, parallel to the gulf coast.
The geology and topography of the Loreto region, extending from Bahía Concepción to Agua Verde, is a coastal belt consisting “mainly of a narrow belt of ridges, valleys, and pediments adjacent to the escarpment, low- to moderate-elevation ranges transverse to the coast, and narrow coastal plains”.
Climate
Loreto’s climate is hot and humid, with abundant sunshine (desert with some rainfall in summer).
The median temperature is 24.4 °C (76 °F). The temperatures are hot from June through October. These summer days have highs around 34 °C (93 °F) and high humidity.
In spring season, the temperatures are moderate and temperate.
Autumn and winter months are usually windy.
From January to March, winds blow from the NW (night hours) and the North (day hours), the rest of the year, the winds blow usually from the West.
Loreto’s yearly precipitation is low; averaging about 160 mm (6.3 in). The wettest months are August and September, when there are occasional short-lived rainfalls.
One concern for Loreto is the Pacific hurricane season, which runs from June 1 to November 30, and some times causes heavy rainfall and floods in the area. The last time the town area was hit by a hurricane was on September 2 and 3, 2006, when the hurricane John hit the Baja California Peninsula.
History & Timeline
Loreto was the first Spanish colonial settlement of the Viceroyalty of New Spain on the Baja California Peninsula.
The town was founded in 1697 by Jesuit missionaries, who found a steady spring of fresh water on this site, as the Misión Nuestra Señora de Loreto.
The Jesuits were expelled in 1767, and control of the Baja California missions was given to the Franciscans.
In 1769, the Franciscans were ordered to turn over the Baja missions to the Dominican order and accompany the expedition of Gaspar de Portolà to establish new missions in the unexplored northern frontier that became Alta California. The expedition departed from Loreto on March 24, 1769.
The town served as the capital of the province of Las Californias from its founding until the capital was moved to Monterey on February 3, 1777.
In 1768, the province had been split into Alta California (today’s U.S. state of California) and Baja California. At first, the two provinces continued with a single governor. Later, the town became the headquarters for the Lieutenant Governor of California Viejo (the province of Baja California).
Tourist Attractions & Sightseeing
There are seven buildings in Loreto from the 18th to the 20th century that are considered historical monuments by the federal government; the most important is:
The Mission of our Lady of Loreto, which is at the start of El Camino Real (“The Royal Road”).
Historic corridor that follows north along the ancient route of the Spanish missions, to its ending in Sonoma, California, USA.
In the neighboring town of San Javier are five historical buildings, most important of them are:
Mission of Saint Francis Xavier (Misión de San Francisco Javier), the best preserved mission in the peninsula.
The ruins of Mission of San Bruno, the first mission of Baja California, founded in 1683 by Jesuit missionary explorer Padre Eusebio Kino. It was ordered abandoned by the Spanish Crown a mere two years later. It is located twenty kilometers north of Loreto.
The Jesuit Missions Museum (Museo de las Misiones Jesuíticas) is located beside the Mission of our Lady of Loreto. It has a collection of religious art, weapons and tools from the 17th and 18th centuries that were used in the Spanish missions in Baja California.
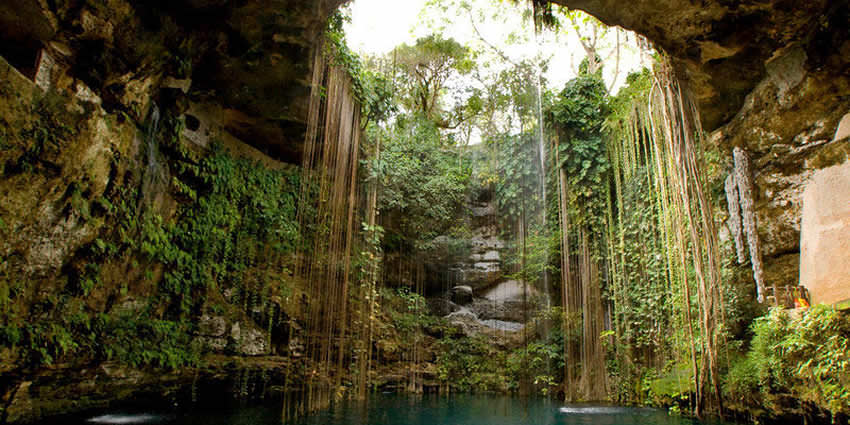
In the “La Giganta” Mountain Range (“Sierra de la Giganta”), there are cave paintings in canyons and rock shelters. The nearest sites to Loreto are “Cuevas Pintas” (15 km to the west) and “La Pingüica” (60 km to the North).
The cave paintings from the indigenous groups of Baja California are world-famous and some of them have been added to UNESCO’s list of world heritage sites.
Beaches & Water Activities
Fishing
Loreto has a reputation as an excellent sport fishing location. This is its main tourist attraction, as well as the main source of employment in the area, thus linking Loreto’s economy closely to fishing.
There are two well-defined fishing seasons:
- summer features “dorado” and species like marlin (black marlin, Atlantic blue marlin, striped marlin) and sailfish, which are ideal for fly fishing
- winter fishing features “yellow tail” (jurel) and other species that usually are deep in the sea rocks
In addition to these seasonal species, Loreto’s waters are home to other species like snapper and seabass, which are found all year long.
Thanks to this abundance, Loreto has been home of several IGFA records. The two “foundations” of Loreto’s sport fishing are the “dorado” and the “yellow tail” (Seriola lalandi dorsalis).
The dorado is the emblematic species of Loreto’s warm waters, its season beginning in late May, peaking from July to September, and ending in November, with two important tournaments, in July and September.
The yellow tail is one of the strongest species; its season begins in November, peaks from March to April, and comes to an end in late May.
Traditions, Holidays & Festivals
- Fiestas de la Virgen de Loreto. The Our Lady of Loreto Festivities are celebrated on September 8. It’s a series of religious, civic and cultural events.
- Fiestas de la Fundación de Loreto. The foundation of the city is celebrated from October 19 to 25. It’s one of the most important cultural events in the state.
- Fiestas de San Javier. The festivities from December 1 to 3 are in honor of Saint Francis Xavier, patron saint from the neighbor town of San Javier. These festivities attract a lot of pilgrims from the peninsula.
- Loreto 400. An off-road racing event that takes place in September. The course is a classic desert offroad race which route includes Comondú, San Javier and the old towns of La Giganta mountain range.
- Loreto 300 milles. Off-road racing event. December.
- Torneo de las Mision Fishing Charity Tournament that started in 1993. The 2007 edition will be July 12–14.
- Loreto Dorado International Fishing Tournament. Takes place in July.
- Copa Dorado Tournament. State tournament in September.
- Governor’s Cup Fishing Tournament. May
How to get there & Transportation
The city is served by Loreto International Airport, offering domestic flights on carriers Aeromexico, AeroCalafia, and Aeroservicio Guerrero.
It is also one of the few places to get aviation fuel in the Baja area. International service is currently provided by Alaska Airlines and Horizon Air to Los Angeles.
Tourist Assistance + Emergency Numbers
You can dial 078 from any phone, where you can find free information about tourist attractions, airports, travel agencies, car rental companies, embassies and consulates, fairs and exhibitions, hotels, hospitals, financial services, migratory and other issues.
Or dial the toll-free (in Mexico) number 01-800-006-8839.
You can also request information to the email correspondencia@sectur.gob.mx
MORE EMERGENCY NUMBERS:
General Information: 040 (not free)
National Emergency Service: 911
Radio Patrols: 066
Police (Emergency): 060
Civil Protection: +52(55)5683-2222
Anonymous Complaint: 089
Setravi (Transport Mobility): +52(55)5209-9913
Road Emergency: 074
Cruz Roja: 065 o +52(55)5557-5757
Firefighters: 068 o +52(55)5768-3700
Let us know if this article was useful for you