Cenote vs Grotto – What’s the difference?
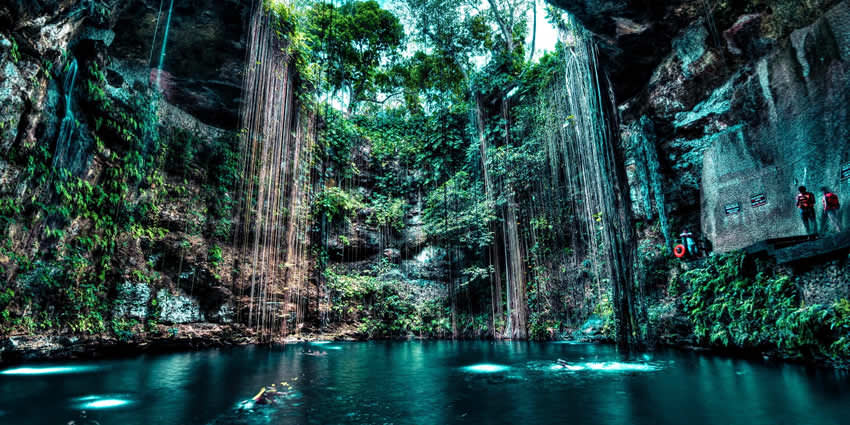
Cenote is a water-filled sinkhole in limestone areas
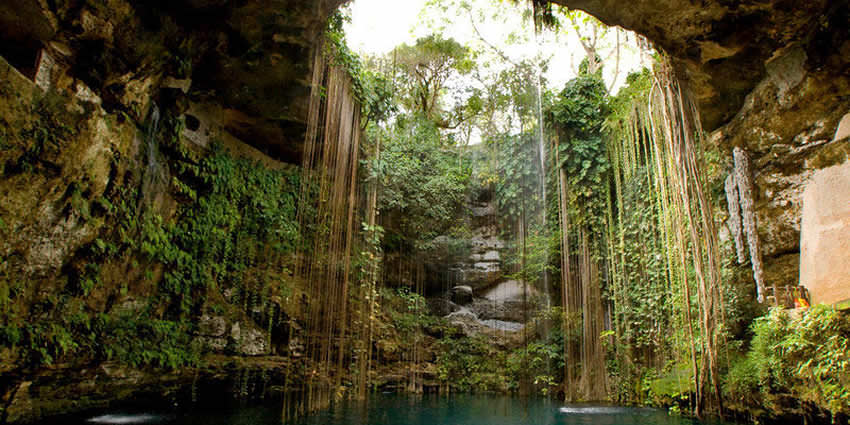
A cenote is a natural sinkhole or deep natural well formed by the collapse of surface limestone, exposing groundwater underneath. These underwater caverns are particularly prevalent in the Yucatan Peninsula of Mexico.
Some cenotes are open-air and others are located within caves.
The water in cenotes is often crystal-clear, creating a captivating and refreshing environment. Historically, cenotes held cultural significance for the ancient Maya and were sometimes used for sacrificial offerings.
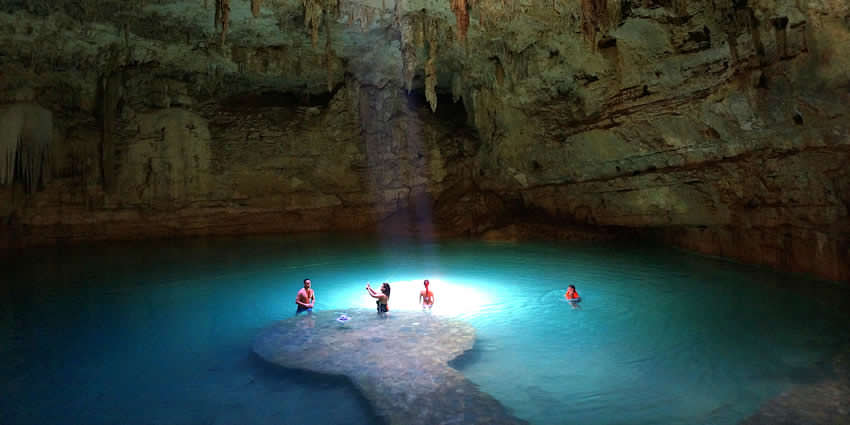
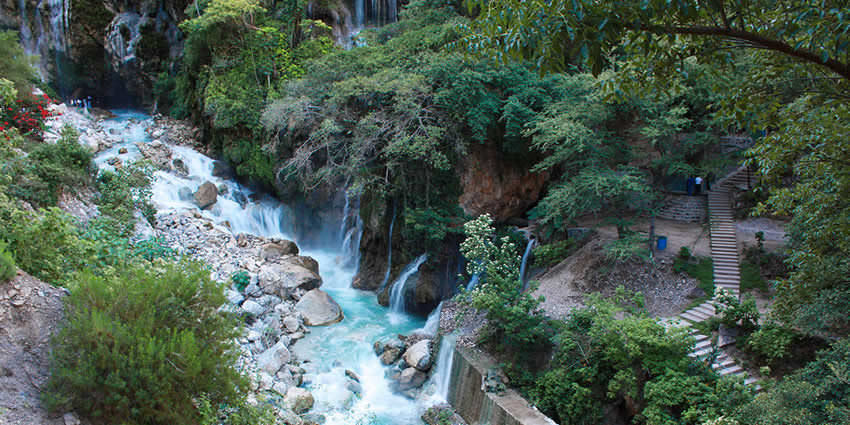
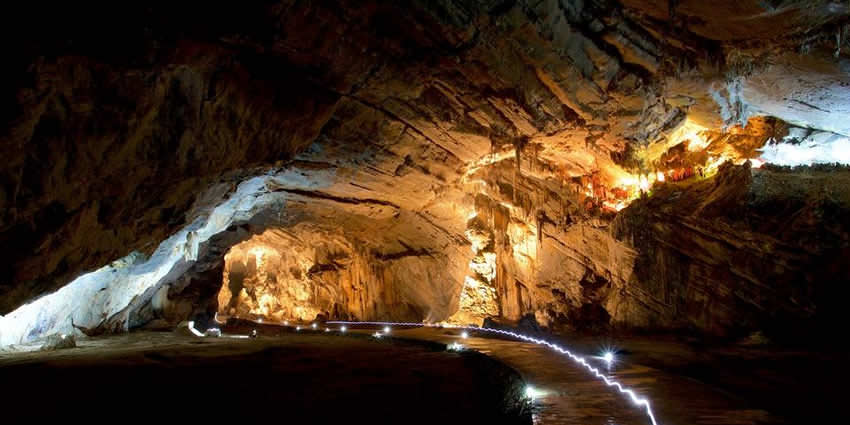
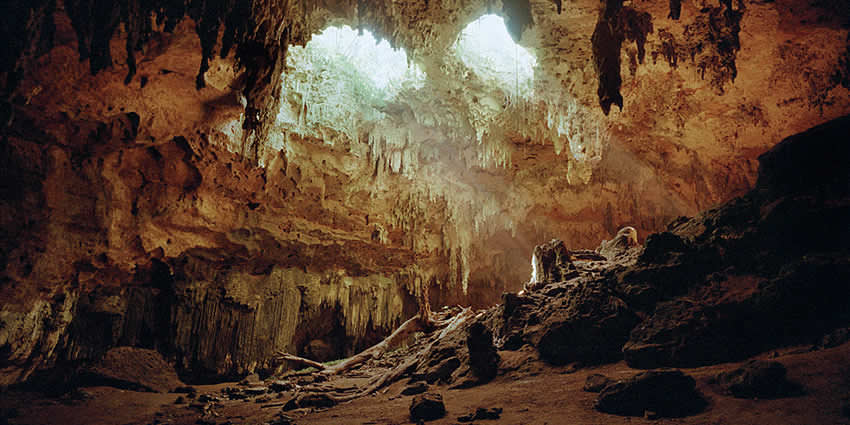
Grotto is a small cave or cave-like structure
Grottoes can be located both above ground and underground, some with unique rock formations such as stalactites and stalagmites, and can vary in size and complexity, ranging from small caves to extensive cave systems.
Once all these grottoes and cenotes were used by the Mayans for human sacrifices.
When you visit Mexico, take the time to discover these unique geological wonders, and be sure to respect and preserve the fragile ecosystems that make cenotes and grottos so enchanting for generations to come.